While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. If a company keeps accurate records using the double-entry system, the accounting equation will always be “in balance,” meaning the left side of the equation will be equal to the right side. The balance is maintained because every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts. For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease.
How does the Accounting Equation work?
As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets. So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity). The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. While a company’s balance sheet records cash entries, it can’t track cash flow. The income statement and balance sheet typically use the accrual method of accounting, which means transactions are made, but money may not be collected or paid out yet.
Example of a Balance Sheet
Assets represent the valuable resources controlled by a company, while liabilities represent its obligations. Both liabilities and shareholders’ equity represent how the assets of a company are financed. If it’s financed through debt, it’ll show as a liability, but if it’s financed through issuing equity shares to investors, it’ll show in shareholders’ equity.
What Is Included in the Balance Sheet?
- For example, imagine that a business’s Total Assets increased by $500.
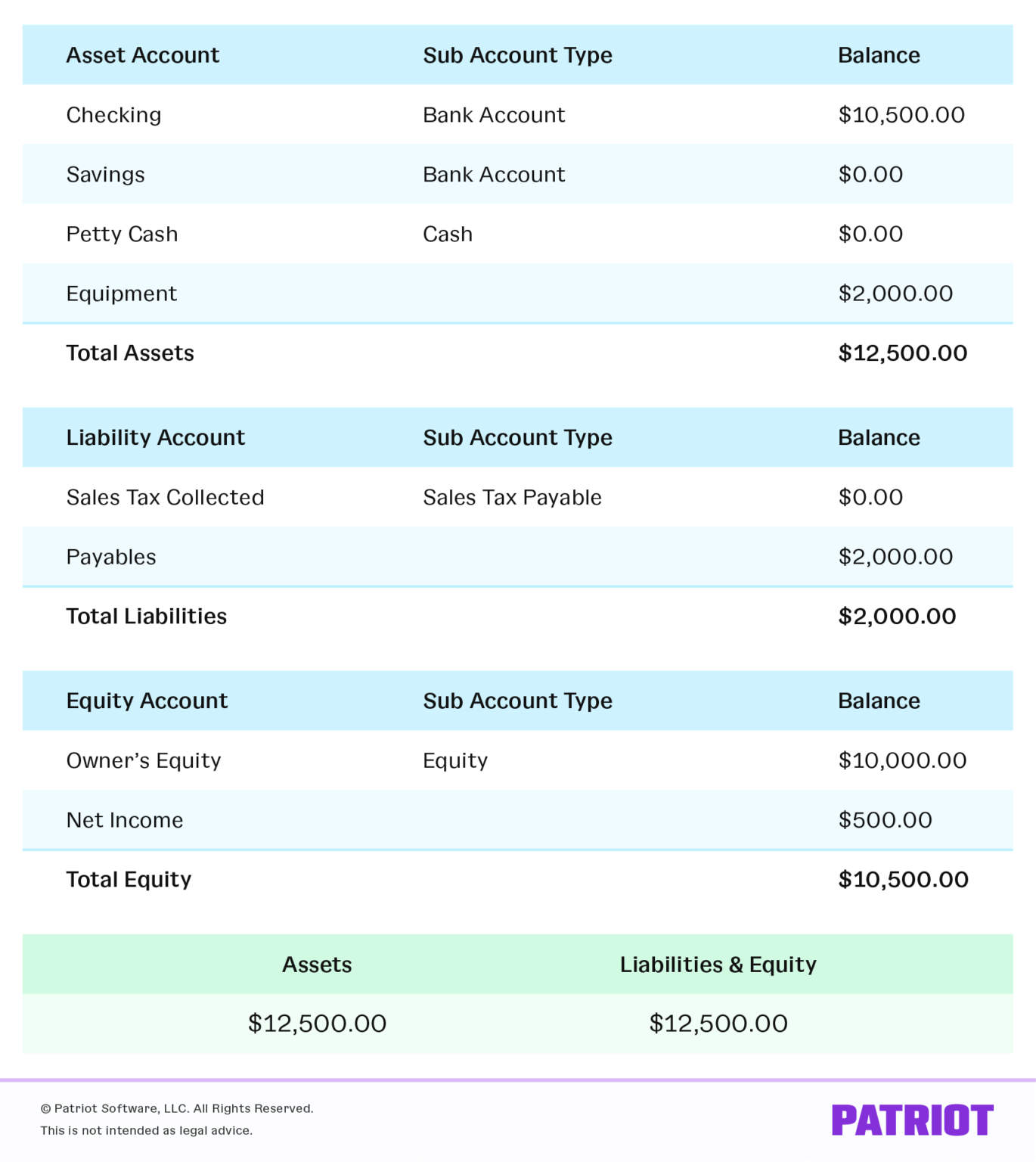
- At any moment in time the Accounting Equation must balance.
- We could also use the expanded accounting equation to see the effect of reinvested earnings ($419,155), other comprehensive income ($18,370), and treasury stock ($225,674).
- When analyzed over time or comparatively against competing companies, managers can better understand ways to improve the financial health of a company.
- Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts.
‘Retained earnings’ are also earnings that have not been paid to shareholders via dividends. Suppose you decide that if you offered coffee as well, you’d probably get more doughnut sales. The loan from your cousin is a liability because the business is obligated to pay it back. Cash (asset) will reduce by $10 due to Anushka using the cash belonging to the business to pay for her own personal expense.
Real-World Examples of the Expanded Accounting Equation
Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can xeros covid be recorded in a similar way. This equation is behind debits, credits, and journal entries. To make the Accounting Equation topic even easier to understand, we created a collection of premium materials called AccountingCoach PRO.
Examples of assets include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid insurance, investments, land, buildings, equipment, and goodwill. From the accounting equation, we see that the amount of assets must equal the combined amount of liabilities plus owner’s (or stockholders’) equity. As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect.

If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value. ‘Retained earnings’ is money held by a company to either reinvest in the business or pay down debt.
Debits and Credits are the words used to reflect this double-sided nature of financial transactions. Liabilities are the stuff that a business owes to third parties. Along with Equity, they make up the other side of the Accounting Equation.

